Main Concepts of 3D Copy |
|
Objects of Copy
The collection of copied objects of a single operation can contain several elements of the same type (only operations, only Bodies, only faces, etc.). Depending on the type of the 3D copy (i.e. on the type of the selected objects of copy), parameters and capabilities of the operation will be changing (see Types of Copies section).
Source and target coordinate systems
Any existing LCS can be selected as the source and the target coordinate systems. If the required LCS (source or target) is not found in the 3D model, it can be created when defining the 3D copy. To do this, just select a 3D point as the origin for the LCS being created. A new 3D element – LCS will be created at this point. The axes of the newly created LCS will be directed along the axes of the global coordinate system.
General Principles of Copying
The position the copy being created is defined in a general case by carrying the source coordinate system over the target one.
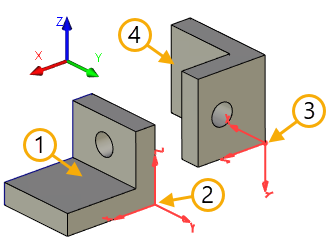
1. Source object of copy - operation
2. Source coordinate system
3. Target coordinate system
4. Copy
The copy being created can be additionally subjected to symmetry (mirroring) about one of the principal planes of the target coordinate system.
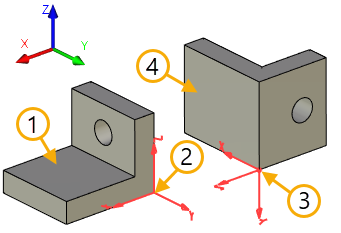
1. Source object of copy - operation
2. Source coordinate system
3. Target coordinate system
4. Copy with additional mirroring about the plane XY of the target coordinate system
When creating a copy with additional mirroring, one can specify just the source LCS. In this case, the system assumes that the source and the target LCS coincide.
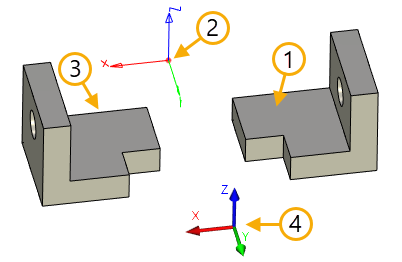
1. Source object of copy - operation
2. Source coordinate system
3. Copy with additional mirroring about the plane YZ
4. Global coordinate system
The additional mirroring of the copy produces the result similar to that of the 3D Symmetry operation. Such copies can be used, for example, for creating symmetrical parts. You create the half-part first, then do copy with mirroring, and, finally, the Boolean addition of the two halves.
When creating a 3D copy, you can refuse the new body creation. In this case, the operation results in moving the source body.