Representations Tab



Representations Tab |
  
|
Representation is a set of rules (for example, grouping and sorting) for displaying Product structure data in various forms and further usage in generating report tables. One product structure may have several representations that correspond to different report tables.
All the conditions specified on Representations tab work only in ![]() Apply product structure representation mode.
Apply product structure representation mode.
All existing representations are displayed in the corresponding field.
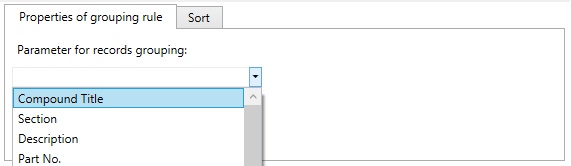
Properties of each representation are managed on Grouping rules and Representation properties tabs. The Grouping rules are managed on Properties of grouping rule and Sort tabs.
The following flags are located near representations names: Use for positions assignment ![]() , Consider records hierarchy while grouping
, Consider records hierarchy while grouping ![]() , Use position column
, Use position column ![]() .
.
Representation Properties
You can specify common representation properties on Representation Properties tab.
Consider records hierarchy while grouping. If the flag is set, the grouping will be performed separately on each level of hierarchy. It allows to assign positions and receive reports for different “branches” of the product structure tree if necessary. The flag is not available when Use for variant reports flag is active.
Important! It is required the topmost record of the product structure tree to be included into reports of the current document for correct data processing in this mode.
For example, you want to create BOM table only for the “1.1” subassembly. For this purpose, you need to select it in the product structure and create report with Only selected elements and Only first level parameters.

More information about reports creation can be found in “Reports Tab” section.
Ignore option “Include in product structure”. If the flag is set the representation will show records with disabled Include in product structure option.
Filter. Specifies the filter set on the Filters tab that will be used for the current representation. The drop-down list contains filters from Filters tab.
Synonym name. You can specify a synonym name for the representation. The synonym name may be helpful if you plan to output summation results in Summation results window or link them with variable.
More information about the window can be found in “Summation result” section.
Use for positions assignment. If the flag is set, positions for representation are assigned automatically. Otherwise, positions will not be assigned for this representation Note, that this flag will be used in combination with analogous flags for automatic position assignment set for each grouping rule if any exists.
Use “Position” column. If the flag is set, the specified position is entered into “Position” column. If the flag is not set, the position is entered in the column specified in Column for position field.
Positions will not be displayed in the product structure if the flag is not set and the column name is not specified.
If flag Assign positions automatically is not set, this flag will be ignored.
Use for variant reports. When the flag is set, the representation data is processed in a specific way to generate a variant report. Report type can be selected from the drop-down list of Type of variant report field.
More information about variant reports can be found in “Variant report creation” chapter.
Grouping Rules
Rules for grouping records in the product structure window are specified on Grouping rules tab.
You can set name for a grouping rule. For each grouping rule there is also possible a set of positioning options: create positions for group, positions increment, number of skipped positions at the beginning and number of skipped positions at the end of the group.
Every grouping rule has its type. According to the grouping rule type, you may set additional options on Properties of grouping rule tab.
The following types are available:
By condition. You may specify one or several conditions for the rule. Conditions are similar to the filters from the Filters tab.
By parameter. When you create this type of grouping rule, you can select column from the drop-down list. Records will be grouped according to the values in this column.
Values from the column will be used as groups names if the flag Consider records hierarchy while grouping is not set.
By BOM sections. Product structure records will be grouped by BOM sections. Each section is included into a separate group. BOM sections are defined in BG: Edit BOM sections command.
By default. This type merges all records into one group.
If there are several grouping rules in one representation, they are applied sequentially. Initially the first rule that distributes records to the groups is applied. Some of the records may be not included in any group after that. The second rule is used for these records. The following rule is used for the remaining “Free” records and so on.
Sorting
Sorting can be specified for each grouping rule (group) on the Sorting tab.

To create a new sorting rule at first you need to select a grouping rule. Then, you need to create a sorting rule using icon ![]() Add. You can select column name in the Column field from the drop-down list. The data will be sorted by this column. After that, you need to select limits of comparison region for the columns.
Add. You can select column name in the Column field from the drop-down list. The data will be sorted by this column. After that, you need to select limits of comparison region for the columns.
From – defines the beginning of the comparison region.
|
You can select one of the following values from the drop-down list: character № - the character serial number. For example, three will mean that comparison region will begin from the third character of the selected column string. substring – the serial number of the selected character sequence occurrence, for example, from the first substring “Part” occurrence. character № from end – the character serial number from the end of the string, for example, the third char from the end. substring from end – the serial number of the selected character sequence occurrence from the end of the string, for example, the first appearance of “ISO” substring from the end. |
№ - the serial number of the string or substring.
“ ” – the sequence of substring characters here. |
|
To – defines limits of comparison region.
|
character № - the character serial number. substring - The serial number of the selected character sequence occurrence, for example, to the first appearance of the “-” substring. end of string –all characters to the end of string will be compared. |
Compare. The field specifies comparison type.
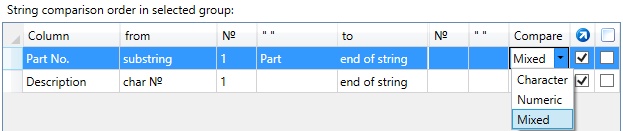
Character –content of two data cells of the table will be compared as two character strings.
Numeric – content of two data cells of the table will be compared as two numeric values. If string contains non-numeric characters they will be omitted on comparison.
Mixed – The strings will divided into substrings that contain character and numeric values. After that, same-type substrings will be compared.
If sorting rules for the group are not set, the records of the product structure will be placed in an arbitrary order.
Important! The order of applying sorting rules depends on their order in the list.
Position priorities
- If both numbers and characters are located on the same position in the data cells, the priority goes to numbers;
- If there are character sets “AA” and “AAA” on the same position, priority goes to the shortest record.
Example of sorting creation
Sorting will be set for the “Part No.” column for all records in the “Grouping rule_1” section.
Each data cell of “Part No.” column will be searched for the first “Part” substring from the beginning.
Searching is performed to the end of string. Type of comparison is set to Mixed, i.e. all characters and numbers after the specified substring will be taken into account.
The data was inserted into the table after specifying the sorting conditions. They are sorted by order of creation.
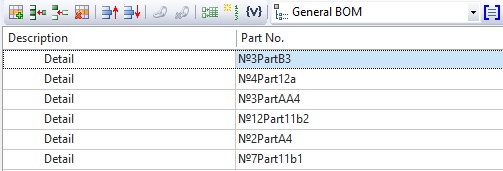
After activation of ![]() Apply product structure representation mode, the sorting rules were applied to the records of the “Part No.” column.
Apply product structure representation mode, the sorting rules were applied to the records of the “Part No.” column.
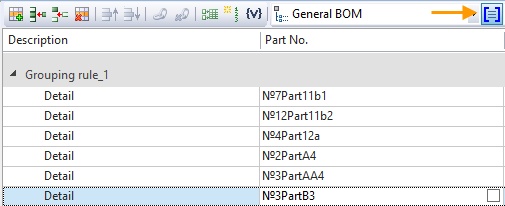
The characters and numbers before Part substring were not taken into account.
Initially the comparison was made by the first position after the Part substring.
Numbers on the first position were selected from each cell (1). They were combined into substrings with nearby numbers (11, 12). After that, they were compared.
Then all chars on the first position were selected (A, B). They were combined into substrings with nearby characters, if available (AA). They were compared.
Then symbols on the second position were compared and so on until the end of the string.