Filtering Records in Representations of Product Composition |
|
Filters define conditions of displaying data in representations. For example, from the whole set of product composition records you can select only records containing materials to receive the corresponding report. The same filter can be used in multiple representations. In order to apply a filter, you should select it in the Filter drop-down list, which is located in Representation Properties.
Filters can be created and customized in the eponymous tab of the ![]() Product Composition Parameters and
Product Composition Parameters and ![]() Product Composition Types windows. the tab is split into two sections. The upper section contains the list of filters, the lower section contains properties of the filter selected in the list. Filters can be selected in the list using
Product Composition Types windows. the tab is split into two sections. The upper section contains the list of filters, the lower section contains properties of the filter selected in the list. Filters can be selected in the list using ![]() . A row of the selected filter gets highlighted.
. A row of the selected filter gets highlighted.
Buttons of following commands are available to the right of the filters list:
![]() Add <Ctrl>+<N>
Add <Ctrl>+<N>
Adds a new filter to the bottom of the list. Upon calling this command, a pop-up appears, where you have to select a type of filter.
![]() Delete <Del>
Delete <Del>
Deletes selected filter.
![]() Copy <Ctrl>+<C>
Copy <Ctrl>+<C>
Copies selected filter into clipboard.
![]() Paste <Ctrl>+<V>
Paste <Ctrl>+<V>
Pastes a filter from clipboard.
![]() Up and
Up and ![]() Down
Down
Move selected filter up or down the list. The order of filters in this list defines the order in the Filter drop-down list in Representation Properties and does not affect filters application.
Some of the mentioned commands are also available in the contextual menu of a filter.
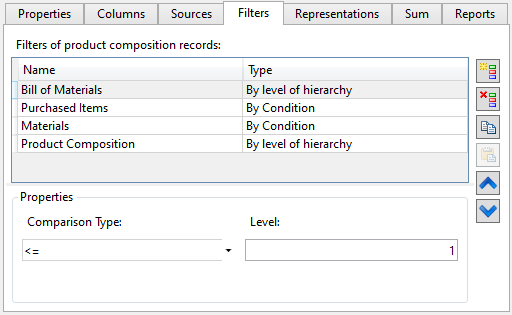
Following parameters are displayed for each filter in the list:
Name
Name of a filter. Any arbitrary set of symbols can be inputted via keyboard as a name. In order to rename a filter double-click ![]()
![]() its name.
its name.
Type
Method of data filtering. Filters of different types have different properties. Following types are available:

•By Condition
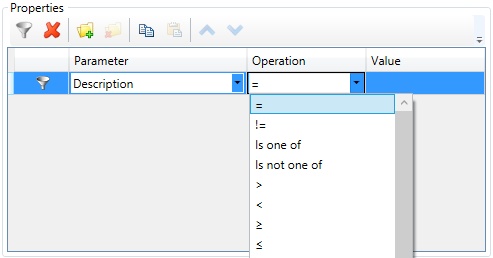
This type allows to check if the content of one of the product composition columns fulfills specified conditions.
Conditions are set in the same way, as when filtering data sources. The only difference is that the Parameter drop-down list contains names of columns of the product composition.
•By level of hierarchy
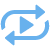
This type of filters helps to define level in assembly hierarchy for which to gather product composition data.
You can specify Comparison type and Level for this filter. The levels values begin from “0” (the product is on a zero level). For example, filter “<= 1” will gather data in the assembly file and the fragment files of the first level.