Constraints > Linear Array |
|
This constraint is automatically created for a one-dimensional Linear array and Copy with Translation. This constraint is indicated by the ![]() icon near second copy in array. Due to the constraint, during parameterization and editing, the drawing lines created by the array, retain the relations that was set by the linear array: equal step and alignment on a single line. To create this constraint, the array command should be created in the Create copies with constraints mode.
icon near second copy in array. Due to the constraint, during parameterization and editing, the drawing lines created by the array, retain the relations that was set by the linear array: equal step and alignment on a single line. To create this constraint, the array command should be created in the Create copies with constraints mode.
|
<Ctrl+F> |
Example
Applying Constraints and Driving Dimensions to Linear Array Elements
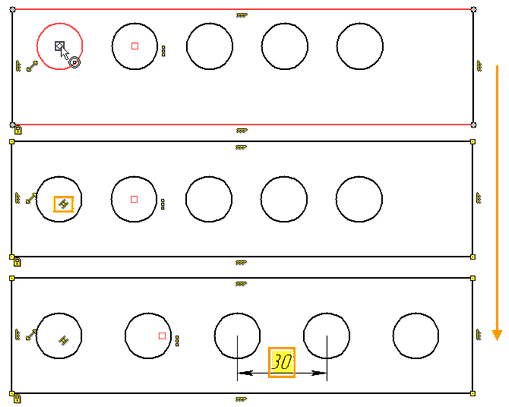
Suppose we are given a rectangle (built with constraints and with a fixed point), on the left side of which there is a circle. Using the Linear array command, copy 5 circles inside the rectangle. We check that the Infer Constraints mode is enabled in the sketch, then through the context menu, by clicking ![]() on the circle, we call the Linear array command. Check that the Create copies with constraints mode is active. Specify the number of copies as 5, choose the starting point of the array, direction and step. As soon as the array was built, a Linear array constraint was automatically created. A constraint icon has appeared on the drawing
on the circle, we call the Linear array command. Check that the Create copies with constraints mode is active. Specify the number of copies as 5, choose the starting point of the array, direction and step. As soon as the array was built, a Linear array constraint was automatically created. A constraint icon has appeared on the drawing ![]() .
.
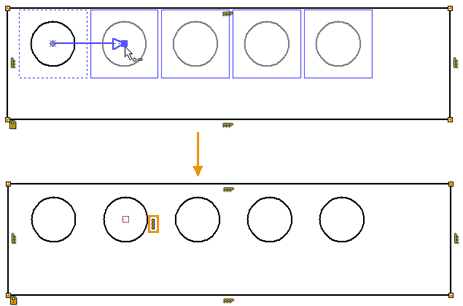
Fix the length of the left side of the rectangle, and position the horizontal axis of the array in the middle of the rectangle using the Middle constraints.
Choosing the constraint Middle with the help of ![]() we specify the upper segment of the rectangle, then the lower one, and then the center point of any circle, for example, the first one. After entering the constraint objects and completing the command, all the elements of the array, according to the Linear array constraint, were moved as a whole.
we specify the upper segment of the rectangle, then the lower one, and then the center point of any circle, for example, the first one. After entering the constraint objects and completing the command, all the elements of the array, according to the Linear array constraint, were moved as a whole.
And also change the array step by setting the driving dimension. To change the array step, you can put a driving dimension between any points of two circles. For example, put the dimension between the centers of the third and fourth circles. By changing the dimension value, the user also changes the step for all elements of the array, since all array elements are bound by a Linear array constraint.