Solid Body |
|
This chapter provides list of operations for solid 3D modeling in the T-FLEX CAD system as well as common options available during creation of such operation, and gives a short description. Along with solid 3D modeling many operations listed here may be used for surface modeling. Basic operations require selection of auxiliary 3D construction entities used for setting the shape of future bodies and surfaces. Other operations use existing solid bodies and surfaces for creating more precise shape. Depending on their location in the T-FLEX CAD interface, operations may be divided into following categories:
•Main Operations
Commands for creating main operations are available in the Operations and Advanced groups of the 3D Model ribbon tab. Brief description of such operations can be found in the current page below, detailed descriptions of working with such operations and interface of their creation and editing commands can be found in the dedicated topics of the current chapter, except the arrays, which are described separately.
•Special Operations
Special operations may be divided into following subcategories:
oPrimitives
Operations for creating basic geometric bodies (Box, Cylinder, Cone, Sphere, Torus, Prism, Pyramid) without using additional construction elements.
oSurfaces
Operations for working with surfaces and faces of bodies.
oSheet Metal
Operations for creating bent and stamped sheet metal elements.
oDeformation
Operations allowing free-form body or surface shape editing.
Each of the subcategories listed above correspond to drop-down list of commands in the Special group of the 3D Model ribbon tab. Moreover, each of the subcategories, except Deformation, have its own ribbon tab with corresponding name.
•Assembly operations
Commands for creating 3D Fragment, Adaptive Fragment, External Model and 3D Picture operations, which provide variety of ways to insert 3D geometry from other documents, are available in the end of the Advanced group of the 3D Model ribbon tab. Moreover, there is the Assembly tab in the ribbon dedicated to them. Descriptions of working with such operations and interface of their creation and editing commands can be found in the separate chapter.
Extrusion
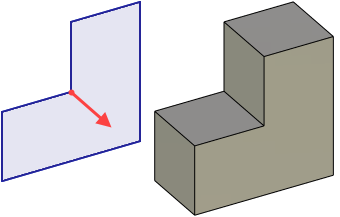
Extrusion operation yields a body or surface formed by straight propagation of a contour along a specified direction. Extrusion can be performed along not only the extrusion vector, but along normal direction to the contour in either or both directions as well. Thus, it provides a means of thickening an arbitrary face, even a non-planar one. Extrusion can also be limited from face to face, from surface to surface or through the whole volume of the selected body.
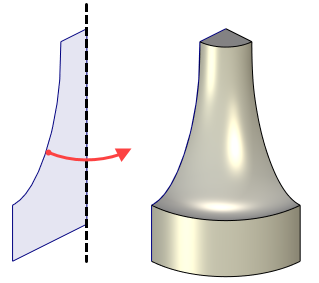
Rotation
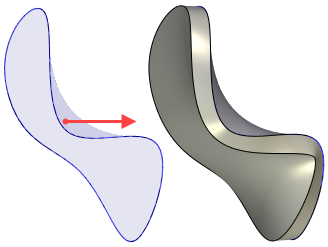
Rotation operation yields a body or surface formed by revolving a contour around an axis located in space for a given angle. The original contour can be located in an arbitrary orientation relative to the axis and lay in arbitrary plane, but it should not intersect the axis.
Blend
Edge blend is an operation for creating transitions between two or more adjoining faces belonging to one solid body or surface. Face Blend is an operation for creating transition surface between two sets of smoothly meeting faces. Three-Face Blend is an operation for creating transition surface between two sets of smoothly meeting faces, where resulting surface will be tangent to the third set of faces.
Boolean
Boolean operation creates a new body based on two or more existing bodies. As a result of the operation, a new body is created that is a combination of the source bodies.
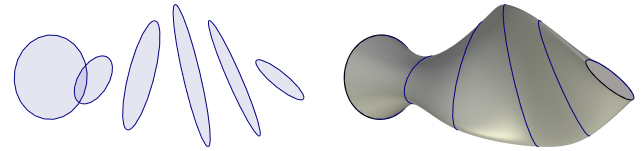
Loft
Loft is an operation for creating new bodies and surfaces of complex geometrical shapes. The resulting spline faces are constructed on the wire guides in one or two directions and according to the specified boundary conditions. The base elements for spline definition can be practically any entities of the three geometrical types: "point", "wire" and "surface". Depending on the base element type, the result will be either a solid body or a set of surfaces.
Operations for geometry creation by moving a contour along defined path
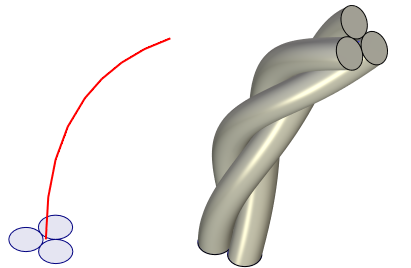
Sweep is an operation that creates bodies or surfaces whose geometry is defined by an arbitrary-shape profile propagated along a spatial curve. The operation provides controls over scaling of the profile and its twisting with respect to the trajectory axis as it moves along.
Pipeline is an operation for creating of pipelines along defined routing and pipeline connection elements according do selected standard.
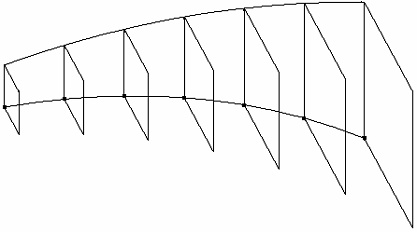
By Parameters operation extends the capabilities of the Sweep operation. The base profile is defined in such a way that its geometry and orientation are driven by a variable. The driving variable can assume values within the specified range. Final body or surface is created as a result of recomputing the geometric shape and orientation of the profile across the whole range of the variable values..

Copy
Copy is an operation for creating copies of existing operations, bodies, 3D construction entities and even sets of faces.
3D Symmetry
3D Symmetry is an operation for symmetrically reflecting selected 3D objects in relation to a given plane.
Array
Array set of operations includes wide variety of operations for creating multiple copies of existing 3D objects with different types of copies placement.
Advanced Operations
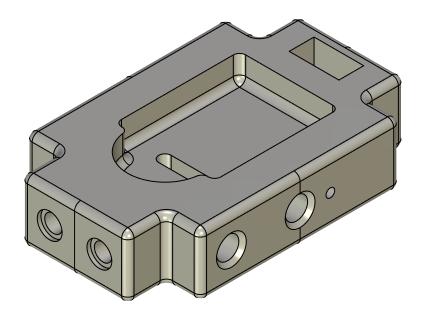
Hole
Hole is an operation for creating standard apertures. It relies on a provided parametric library of holes satisfying current standards. The command supports creation of patterns of holes, holes through multiple bodies, and threaded holes. When a threaded hole is created on a face, a cosmetic thread is displayed.
Shell
Shell is an operation for creating shells on the basis of solid bodies. A shell is a hollow thin-sided solid body with the sides of a certain thickness. When creating shells some faces of the initial solid body can be deleted.
Offset Body
Offset Body is an operation for creating an equidistant non-hollow body whose faces are displaced relative to the initial solid body faces along the normal direction at a set value.
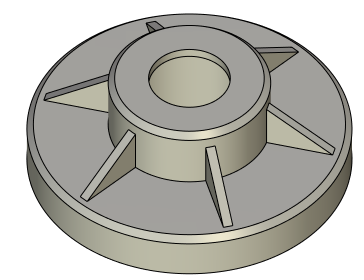
Rib
Rib is an operation for creating ribs of the solid body on the basis of one or several 3D profiles. Execution of this operation results in a solid body obtained via a Boolean operation of a union of the rib being created with the source body.
Cut
Cut is an operation for creating a body or surface by cutting some portions off the original body/surface, or getting two new bodies/surfaces by splitting the original body/surface into two parts.
Thread
Thread is an operation for creating cosmetic threads on cylindrical and conic faces of 3D model. A cosmetic thread is a texture applied to the selected face which depicts the pitch, direction and boundaries of the thread but doesn't provide it's actual geometrical representation.
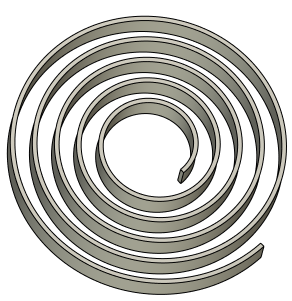
Spiral
Spiral is an operation for creating spiral-like bodies or surfaces by moving an arbitrary-shape profile along a spiral curve. This operation may be used for modeling actual geometry of a thread. However, in most cases, when only cosmetic representation of a thread is needed, the Thread operation is recommended for use instead, as it creates less load on hardware.
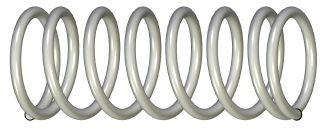
Spring
Spring is an operation for creating spring-shape bodies by moving a round profile along a spiral curve. It differs from the Spiral operation in the capability of forming closed and ground ends of the spring.
Taper
Face Taper is an operation for tapering one or several selected faces at a specified angle, with automatic correction of the adjacent faces. Body Taper is an operation for creating two-sided tapers on faces of a body relative to a specified taper direction and a parting body.
Apply Material
Apply Material is an operation for applying a certain material on one or several model's faces. The applied material will be maintained through the future model modifications despite changes in the face’s geometry.
Simplify
Simplify is an operation for deleting extra edges or vertices from the specified operation body, as well as for simplifying the geometrical base of faces and edges.
Divide
Divide is an operation for dividing operations into separate bodies, that unite several bodies (solid and surface bodies alike). Thus, for example, the result of creating Linear or Circular array or a Boolean operation will be divided by this operation into geometrically separate components.
Topics in this section:
•Loft
•Hole
•Rib